the number of scores that fall below the upper real limit of an interval. … the percentage of scores that fall below the upper real limit of an interval. percentile rank. the percentage of scores with values lower than the score in question. symmetrical. a property of a frequency polygon if when folded in half on the x axis the two sides match.
Tableau Zen
presents data in groups of scores, that fall into certain intervals, and list those intervals in a table. p = f/N. How do you find proportions in a Frequency Distribution Table? percentages = p(100) … The width of each interval should be a relatively simple number. (5, 10, etc) 3.
Source Image: firevoxel.org
Download Image
Statistics Definitions > In statistics, the term “score interval” has two completely different meanings. It can refer to either: Score intervals on frequency distributions, or The Wilson technique to calculate confidence intervals. Definition 1: Score Intervals on Frequency Distributions
Source Image: muscleoxygentraining.com
Download Image
Mathematics 10 Learning Modules Quarter 4 | PDF In which interval would a score of 29.6 fall? In which interval would a score of 19.4 fall? Expert Solution Trending now This is a popular solution! Step by step Solved in 3 steps
Source Image: link.springer.com
Download Image
In Which Interval Would A Score Of 29.6 Fall
In which interval would a score of 29.6 fall? In which interval would a score of 19.4 fall? Expert Solution Trending now This is a popular solution! Step by step Solved in 3 steps IE: in table 2.1 (p. 32), we decided the data should be split into 10 intervals. (176 is the real range). 176/10= 17.6 Since the rest of this data in the table is rounded up to the nearest ones place (the nearest whole number), the interval width should be rounded also to match. 17.6 should be rounded up to the nearest whole number. interval
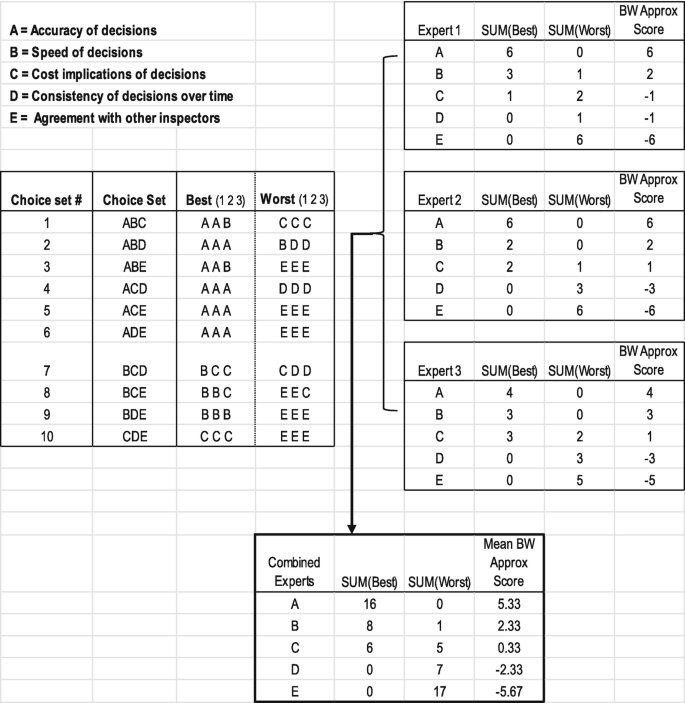
Specialised Statistical Procedures | SpringerLink
In which interval would a score of 29.6 fall? (There is no interval for this number, 20-29, or 30-39) In which interval would a score of 19.4 fall? (There is no interval for this number, 20-29, or 10-19) Also, please don’t forget the graph! Thank you Show transcribed image text There are 3 steps to solve this one. Expert-verified Step 1 Treatment Needs and Service Utilization in Older U.S. Adults Evidencing High-Risk Substance Use – Kathleen A. Fairman, Nicole K. Early, 2020

Source Image: journals.sagepub.com
Download Image
The Midlife Low in Human Beings | naked capitalism In which interval would a score of 29.6 fall? (There is no interval for this number, 20-29, or 30-39) In which interval would a score of 19.4 fall? (There is no interval for this number, 20-29, or 10-19) Also, please don’t forget the graph! Thank you Show transcribed image text There are 3 steps to solve this one. Expert-verified Step 1
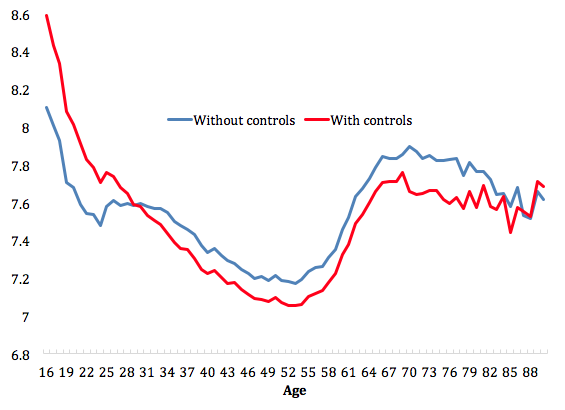
Source Image: nakedcapitalism.com
Download Image
Tableau Zen the number of scores that fall below the upper real limit of an interval. … the percentage of scores that fall below the upper real limit of an interval. percentile rank. the percentage of scores with values lower than the score in question. symmetrical. a property of a frequency polygon if when folded in half on the x axis the two sides match.
Source Image: ugamarkj.blogspot.com
Download Image
Mathematics 10 Learning Modules Quarter 4 | PDF Statistics Definitions > In statistics, the term “score interval” has two completely different meanings. It can refer to either: Score intervals on frequency distributions, or The Wilson technique to calculate confidence intervals. Definition 1: Score Intervals on Frequency Distributions

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
SOLVED: Table 2 Academic Performance Frequency Relative Frequency 0.12 10 to 19 0.08 20 to 29 30 to 39 40 to 49 50 to 59 60 to 69 70 to 79 80 As described above, all the class intervals within a frequency distribution must be of equal width. The formula for determining class intervals is as follows: i ≥ (H − L) / k. Where: i is the class interval, H is the greatest observed value, L is the smallest observed value, k is the number of class intervals. Generally, 5 ≤ k ≤ 15.

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Mathematics 10 Learning Modules Quarter 4 | PDF In which interval would a score of 29.6 fall? In which interval would a score of 19.4 fall? Expert Solution Trending now This is a popular solution! Step by step Solved in 3 steps

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
Last Assignment December 2019 PDF | PDF | Logarithm | Mean IE: in table 2.1 (p. 32), we decided the data should be split into 10 intervals. (176 is the real range). 176/10= 17.6 Since the rest of this data in the table is rounded up to the nearest ones place (the nearest whole number), the interval width should be rounded also to match. 17.6 should be rounded up to the nearest whole number. interval

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
The Midlife Low in Human Beings | naked capitalism
Last Assignment December 2019 PDF | PDF | Logarithm | Mean presents data in groups of scores, that fall into certain intervals, and list those intervals in a table. p = f/N. How do you find proportions in a Frequency Distribution Table? percentages = p(100) … The width of each interval should be a relatively simple number. (5, 10, etc) 3.
Mathematics 10 Learning Modules Quarter 4 | PDF Mathematics 10 Learning Modules Quarter 4 | PDF As described above, all the class intervals within a frequency distribution must be of equal width. The formula for determining class intervals is as follows: i ≥ (H − L) / k. Where: i is the class interval, H is the greatest observed value, L is the smallest observed value, k is the number of class intervals. Generally, 5 ≤ k ≤ 15.